Francesco Taddeo, Michele Emanuele Fortunato, Rosa Turco, Andrzej Kowalczyk, Malgorzata Rutkowska, Lucjan Chmielarz, Vincenzo Russo, Martino Di Serio
Applied Catalysis A: General Volume 707, 25 November 2025, 120521
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2025.120521
Abstract
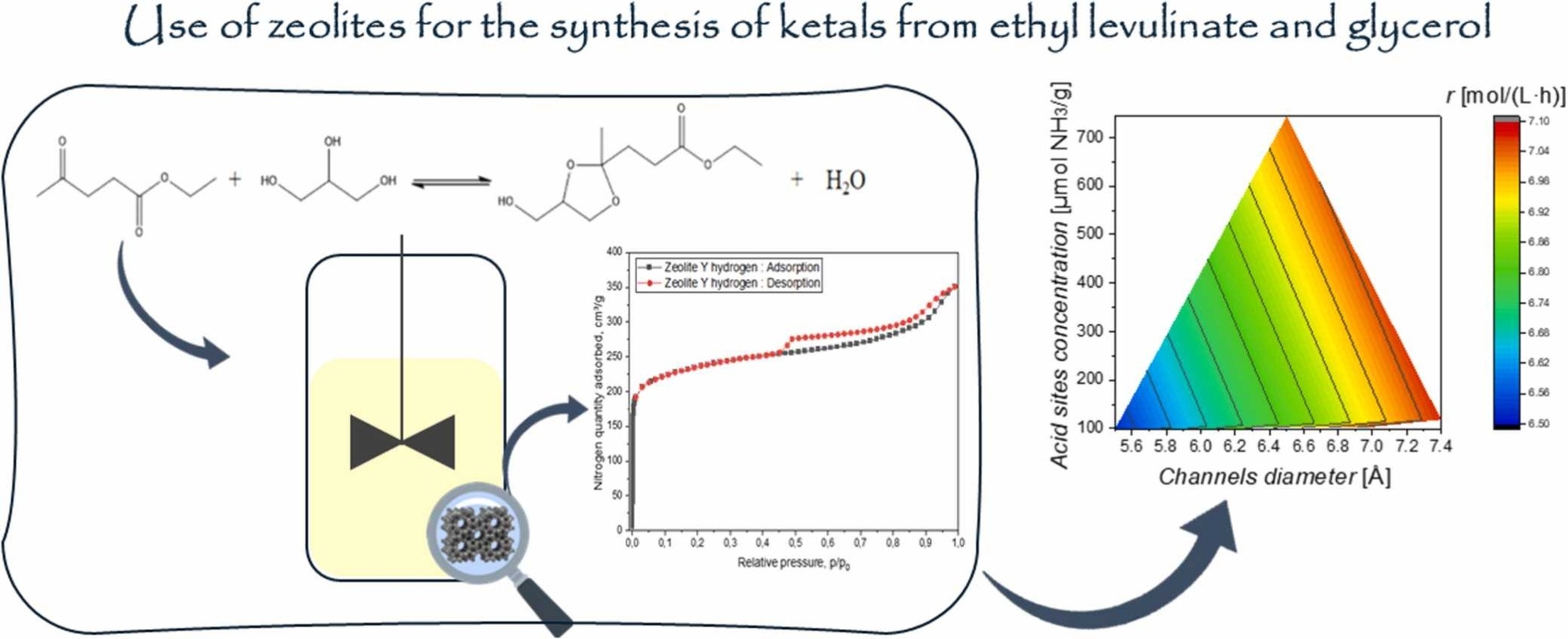
The increasing demand for sustainable alternatives to petrochemical routes has intensified interest in biomass as a renewable feedstock. In this scenario, levulinic acid and its derivatives have gained attention due to their versatile properties. Additionally, glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, also represents a valuable bio-based compound. The reaction between ethyl levulinate and glycerol yields ketal, a product with promising properties for several applications such as solvents, plasticizers, and polymer precursors. Various acid catalysts can be employed in this reaction, and zeolites are particularly attractive due to their excellent mechanical and thermal stability, which enables high catalytic performance. In this study, a screening of different zeolites i.e., H-ZSM-5, H-Mordenite, H-β, and H-Y, was carried out. The catalysts were characterized in terms of elemental composition, surface area, and acid site concentration, and their properties, particularly acidity and channels dimensions, were correlated with their performance in the ketalization reaction. The protonated forms of all the tested zeolites exhibited comparable and remarkable catalytic activity in glycerol conversion.