Stanzione, M., Russo, V., Oliviero, M., Verdolotti, L., Sorrentino, A., Di Serio, M., Tesser, R., Iannace, S., Lavorgna, M.
(2018) Polymer, 149, pp. 134-145.
10.1016/j.polymer.2018.06.07
Abstract
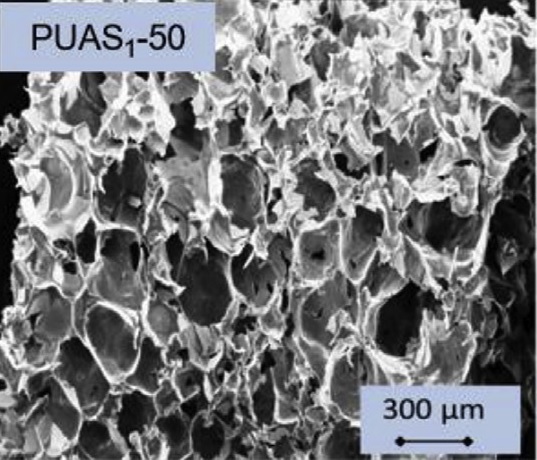
Several bio-based polyhydroxyls are successfully synthesized by using succinic acid, obtained via Arundo donax fermentation and characterized by 1H NMR, GPC, and FT-IR analyses. Furthermore, the bio-based polyhydroxyls, consisting of a wide spectrum of compounds in terms of chemical structure and mo- lecular weight, are used as substitute of conventional polyol in the formulations of Polyurethane and random Urethane-Amide Copolymer bio-based foams. The influence of both amount and typology of bio- based polyhydroxyls on bio-based foam properties is investigated through kinetic analysis, thermo- mechanical characterization, and morphological analysis. The results highlight that the replacement of conventional polyol with the bio-based polyester polyhydroxyls affects the foaming process and consequently the final properties of the free-foamed materials. In particular, the compressive modulus increases by about 140% for a bio-based polyhydroxyl content of 50 wt% together with an increase in foam density. A further increase of these adducts results in a decrease of the glass transition temperature and the mechanical performances. However, the experimental results demonstrate the potentiality of these